How Does the World’s Brightest Laser Pointer Showcase Laser Tech Wonders?
Introduction
In a world where technology continually reshapes our understanding of science, laser technology stands out as a beacon of innovation and practicality. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a cornerstone of modern technology, the journey of laser development is nothing short of remarkable. This blog explores the fascinating world of lasers, illuminated through the lens of the world’s brightest laser pointer, a marvel of engineering and a testament to human ingenuity.
The Evolution and Applications of Laser Technology
The Evolution of Laser Technology The story of laser technology began in the early 20th century, with scientists exploring the nature of light and its potential applications. From the first ruby laser in 1960 to the advanced diode lasers of today, the evolution of laser technology has been driven by relentless curiosity and innovation. Today, lasers are integral in numerous fields, including medicine, communication, and manufacturing, showcasing their versatility and indispensability.
Introducing the World’s Brightest Laser Pointer In a recent YouTube video, a new milestone in laser technology was showcased: the world’s brightest laser pointer. This device, far from being a simple tool for presentations, represents the pinnacle of laser engineering, pushing the boundaries of what is possible with light amplification.
The Fundamentals of Laser Technology
Understanding Lasers: The Basics
Lasers, an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation, represent a significant advancement in light technology. At their most basic level, lasers work by stimulating atoms or molecules to emit light at particular wavelengths. This process creates a beam of light that is not only highly coherent but also extremely precise and intense compared to traditional light sources. This coherence is a key feature of laser light, allowing the waves to be in phase in terms of both frequency and amplitude, which results in a highly focused and directional beam.
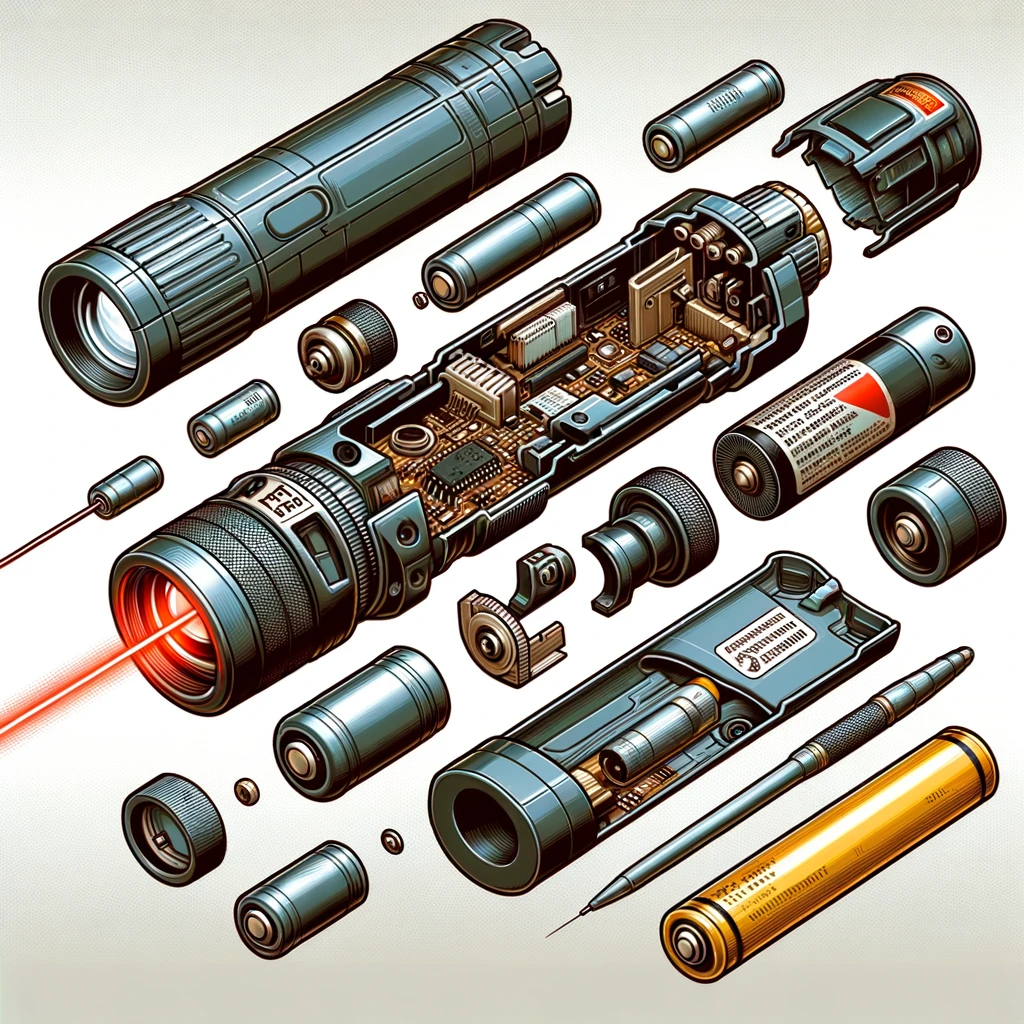
The Anatomy of Laser Pointers
Laser pointers, while simple in design, are perfect examples of laser technology’s practical application. They are composed of three main components:
- Laser Diode: This is the heart of the laser pointer. The diode is a semiconductor device that produces the coherent light. When electricity is applied to the diode, it excites the atoms within, causing them to release photons. The type of material used in the diode determines the color of the laser beam. For instance, a Gallium Nitride (GaN) diode produces blue light, while an Aluminum Gallium Arsenide (AlGaAs) diode emits red light.
- Power Source: Typically a small battery, the power source provides the necessary electrical energy to excite the atoms in the laser diode.
- Focusing Mechanism: This component, often a lens, focuses the emitted light into a narrow, precise beam. The quality of the lens and its alignment with the laser diode are crucial for the pointer’s effectiveness.
Unraveling the Physics Behind Lasers
The Role of Frequency Doubling Crystals
Frequency doubling crystals, also known as second harmonic generation (SHG) crystals, are at the forefront of laser technology, particularly in enhancing the color range of laser pointers. These crystals work on the principle of nonlinear optics, where the frequency of light is doubled, effectively halving its wavelength. This process is pivotal in producing different colors in lasers, especially in the case of green lasers.
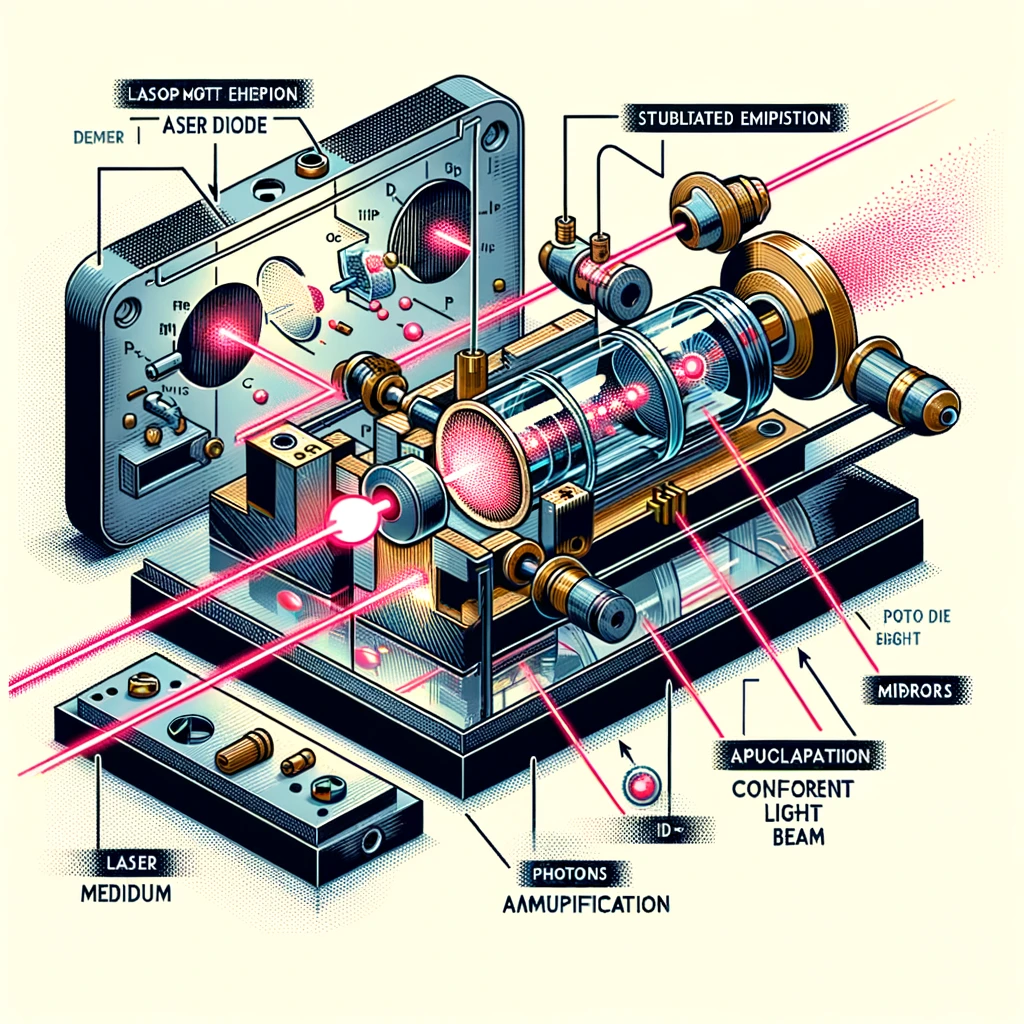
Traditionally, green laser pointers were created by using infrared lasers combined with frequency doubling crystals. The infrared light, typically at a wavelength of 1064 nm, passes through these crystals, which then emit light at 532 nm – a bright green color. This technology has been instrumental in creating high-powered green lasers, which are not only more visible to the human eye but also have various practical applications, such as in astronomy for pointing out celestial objects.
Direct Green Laser Diode Technology
The development of direct green laser diodes represents a significant leap in laser technology. Unlike the traditional method that relies on frequency doubling crystals, these diodes emit green light directly from the semiconductor material. This advancement bypasses the need for frequency doubling, leading to a more efficient, compact, and brighter output.
Direct green laser diodes are made from materials like Indium Gallium Nitride (InGaN), allowing them to emit light in the green spectrum (around 500-540 nm) directly. This direct emission is more energy-efficient and results in a brighter beam compared to the frequency-doubled green lasers. Moreover, these diodes have a longer lifespan and are more reliable, as they have fewer components that could fail.
Applications in Electronic Engineering
Innovating with Microwave Oven Transformers
The use of a microwave oven transformer (MOT) as a power source for the world’s brightest laser pointer is a striking example of innovation in electronic engineering. Microwave oven transformers are robust, high-voltage transformers originally designed to power the magnetron in microwave ovens. By repurposing an MOT, the creator of this laser pointer has demonstrated a remarkable ability to see beyond conventional uses of everyday objects, tapping into their potential for more advanced technological applications.
This approach not only showcases ingenuity but also emphasizes the importance of resourcefulness in engineering. The ability to repurpose an MOT for a laser pointer suggests a deep understanding of the underlying principles of transformers and their potential applications. This kind of innovative thinking is crucial in the field of electronic engineering, where the efficient and creative use of available resources can lead to groundbreaking advancements.
Flyback Transformers in Laser Design
Similarly, the incorporation of flyback transformers, commonly found in older CRT television sets, into the design of high-intensity lasers is another example of cross-disciplinary ingenuity. Flyback transformers are designed to handle high voltages and frequencies, which makes them suitable for applications requiring significant power in a compact form.
In the context of laser design, these transformers provide the necessary high voltage to power the laser diode efficiently. Their ability to manage high-energy pulses makes them ideal for this purpose, ensuring that the laser operates safely and effectively. This application of flyback transformers in laser technology not only highlights the versatility of these components but also underscores the interconnected nature of modern technology, where components from one domain can find innovative applications in another.
The Importance of Safety in Laser Use
The Hazards of High-Power Lasers
The advent of high-power lasers like the world’s brightest laser pointer has brought about a new era in laser technology, but it also introduces significant risks. The intense beam of such lasers is not only capable of causing severe eye damage, including permanent blindness, but it can also be a potential fire hazard. The concentrated energy of the laser beam can easily ignite flammable materials, making it dangerous in certain environments.
Guidelines for Safe Operation
To mitigate these risks, strict safety guidelines must be followed:
- Mandatory Use of Laser Safety Goggles: Specialized laser safety goggles are essential to protect the eyes from the intense light of the beam. These goggles should be specifically designed for the wavelength of the laser in use.
- Avoid Directing the Laser at People or Animals: The intense beam can cause instant damage to the eyes and skin. Therefore, it’s crucial never to point the laser at people, animals, or any living creatures.
- Steer Clear of Reflective Surfaces: Reflective surfaces can unpredictably redirect the laser beam, potentially causing harm or damage to unintended targets.
- Controlled Environment Operation: Operating the laser in a controlled environment where the potential for accidental exposure or damage is minimized is essential. This includes ensuring that the area is free from flammable materials and that there are no unintended targets within the beam’s path.
- Training and Awareness: Anyone operating a high-power laser should be adequately trained in its safe use. This includes understanding the laser’s properties, potential hazards, and emergency procedures in case of an accident.
Demonstrations and Applications of Lasers
Lasers in Everyday Life
Lasers are not just confined to laboratories or industrial settings; they have found their way into our daily lives. From barcode scanners at supermarkets to laser printers in offices, their applications are diverse and far-reaching.

Demonstrations of Power and Precision
The video showcases the laser pointer’s ability to ignite matches, cut through materials, and even engrave patterns, demonstrating both its power and precision. These experiments not only serve as a testament to the laser’s capabilities but also hint at its potential applications in various fields, including manufacturing and material processing.
Future Prospects of Laser Technology
Expanding Horizons in Medicine and Communication
The future of laser technology is incredibly promising, particularly in medicine and communication. In medical fields, lasers offer prospects for less invasive surgeries and new cancer treatments. In the realm of communication, lasers stand to revolutionize data transmission, offering faster and more secure methods.
Environmental and Legal Implications
As we embrace the advancements in laser technology, it’s crucial to consider the environmental impact and adhere to legal and ethical standards. The development and use of high-powered lasers like the world’s brightest laser pointer must be regulated to ensure safety and prevent misuse.
Conclusion
The exploration of the world’s brightest laser pointer offers a glimpse into the vast and wondrous world of laser technology. From its fundamental principles to its wide array of applications, the field of laser technology continues to amaze and evolve. As we marvel at these advancements, we must also navigate the challenges of safety, ethics, and environmental impact, ensuring that this powerful technology is used responsibly and for the betterment of society.
At laserpointernews is dedicated to providing a diverse selection of high-quality laser pointers designed to meet various needs. Whether you’re seeking a laser pointer for professional use, educational purposes, or recreational activities, our collection ensures top-notch performance, safety, and durability.




Leave a comment